By Steven Saint Thomas
There was a lot of talk in 2016 about American progressives moving to Canada in the wake of Donald Trump’s election. They’re talking again. It’s easy to feel on the edge of a society that won’t take climate change seriously, embraces militarism and promotes an economic-growth paradigm that is crippling the planet.
But is Canada really the best destination? Through a lens of sustainability, what look like the best places to live the next 25 years?
There’s a certain randomness to where we live, where we move and where we end up. The two main forces seem to be jobs and family. People leave family for jobs, people rejoin family for – family!
Where would we live if we could pick a place by design?
The ancestors of most Americans migrated here for better economic opportunity – in modern parlance, a job. Native Americans had lived here sustainably for at least 14,000 years.
African Americans also came for jobs, but it was obviously somebody else’s economic opportunity.
In today’s age of easy mobility, most of us look across the country for a good (or better) job and move there. It’s a pretty random process.
I was born in San Diego, for example, because of jobs. My grandparents picked up and left the Midwest in the 1950s to find the land of plenty in burgeoning California.
My wife and I both grew up in San Diego but we moved to Colorado because of a job in 1999. Trudy and I were looking for journalism jobs in our increasingly expensive and unsustainable hometown when my brother (family!) decided to move to Colorado. He persuaded us to look there.
We loaded up a U-Haul, drove to Colorado and leased a house big enough for our family of five, and my brother and his wife. Trudy and I hired on at the daily paper in Colorado Springs.
Random settlement
There was little rhyme or reason in selecting the house we leased in 1999. Like most people, we had a short timeframe in which to find something with enough space in our price range.
In one whirlwind weekend, we found something suitable – but our universe of inventory was whatever people happened to be advertising those two days.
Our lives could have been drastically different, for better or worse, based on the luck of the house-hunting draw.
When our lease was up, we looked for a more diverse neighborhood closer to work. We dabbled in what I call “migration by design” by looking at some 40 houses in the last few months of our lease, taking our time and doing our homework.
Even though we broadened our universe of choices by taking a few months to shop, we still only had a couple of land-selection criteria. The main one was financial: getting a good real estate deal. We found a reasonably priced house and a decent mortgage interest rate.
We lived in the house for 15 years. Then along came permaculture.
Permaculture is an integrated system of designing homes and communities that cooperate with nature. We learned the true essence of sustainability – self-reliant communities free from the globalized, fossil-fuel driven food system.
In 2013, we met permaculture co-founder David Holmgren and toured his 2-1/4 acre homestead in Hepburn Springs, Australia. The property he picked to develop some 25 years ago – Melliodora – was not just a random good real estate deal. Holmgren had first developed a list of criteria and then searched until he found a property that delivered on most of them.
When I looked at my house and my community, it was clear to me I wanted something more than just an affordable mortgage payment.
If I could live anywhere – if I didn’t have a job or family situation that forced me to live in Colorado Springs, where would I go? What kind of community would Trudy and I want? What kind of property would be ideal to settle on?
Our green dream
Holmgren’s land-selection criteria (documented in Melliodora: Hepburn Springs Permaculture Gardens) included both big-picture context and site-specific details. On a geographic level, he was looking for cool, moist climate as well as a community with cosmopolitan sensibilities and prospects for work.
On a micro level, his nine criteria included proximity to a town with schools and culture, a lot between .75 and 2.5 acres for subsistence permaculture gardening, good solar exposure and opportunities for independent water supplies.
What would be on your wish list?
1. Climate: Rainwater. I would want a place with plentiful rain. Colorado Springs gets about 14 inches a year. San Diego gets around 6. From our calculations, we decided the ideal place should get at least 30 inches a year. And no snow! We’d want conditions for year-round cultivation.
2. Scale: Village. We also would want a village. In Australia, we observed permaculturists in four settings: urban, suburban, village and bush (what we would call “countryside”). The cities and suburbs were too crowded for our tastes and tempting fate by having millions of people completely dependent on centralized water and food systems.
The bush, on the other hand, was too remote. It’s hard to develop an interactive, sharing community when you’re 20 miles from the nearest neighbor.
That leaves the village – a small town with less than 15,000 people getting the best of both worlds. There’s still connection to the grid (redundancy is a good thing) and enough people to forge a local economy with the possibility of affordable land.
3. Prospects for work. That means internet access for most of what we do now. Also work in local gardening, teaching, culinary or media would be good.
4. Beauty. Within 10 miles of the ocean would be preferred if the land were affordable!
5. Proximity to family. We have family tied to both San Diego and Colorado. Living in Australia, for example, would be out of the question. We’d like a village with train or bus connectivity to the nearest city.
6. Political will. Could we find a existing community already committed to authentic sustainability and a local economy? Why fight so hard in our middle age to change a place like Colorado Springs when we could join with people already on track?
So, based on these big-picture design criteria, we began a quest in Northern California. Even in a drought, 15 counties in Northern California get 30 inches or more rain. There are lots of small, progressive towns in those coastal counties – Sonoma, Mendocino and Humboldt.
Then I would toss in site-specific criteria:
1. Between 2-5 acres
2. Avoid the San Andreas fault and coastal tsunami zones
3. Biking distance to village center
4. Internet access
5. Ability to capture rainwater
6. Water redundancy from an existing well, spring or utility grid
7. Decent soil with trees for mulch material
8. Existing structure for housing or place for mobile (or tiny) home
9. Sun exposure for solar power
10. Neighbors (hopefully permies) active in barter or trade economy
Sound good? How would you modify the list for your own needs? Migration by design – guess it’s time to stop voting and start looking!




 By Steven Saint Thomas
By Steven Saint Thomas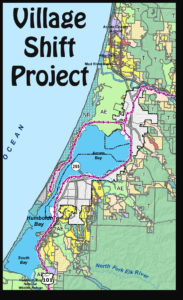 In the past 20 years, I have lived in San Diego (3.4 million people), Colorado Springs (500,000) and now Humboldt Bay (88,000). All these areas are dependent on large, centralized systems to provide water, energy, food and transportation infrastructure.
In the past 20 years, I have lived in San Diego (3.4 million people), Colorado Springs (500,000) and now Humboldt Bay (88,000). All these areas are dependent on large, centralized systems to provide water, energy, food and transportation infrastructure.